(GSI issued this press release in Japanese on March 3rd, 2015.)
Recognizing the importance of accurate positioning of latitude/longitude in people’s lives and economic activities, the United Nations General Assembly resolved on February 26th, 2015 to improve global geodetic reference frame through cooperation with countries all over the world.
This is the first United Nations General Assembly resolution in the field of surveying.
Background to resolution, and relevant points
- In approximately 30% of the world’s countries, their adopted reference frames are not consistent with global geodetic reference frame even now, with inconsistencies between the positions measured by GPS and positions on maps. (Approximately 50% of countries in Asia region) (Fig. 1)
- Rapid spread of smartphones that can measure positions simply by GPS, with number of such smartphones estimated to increase by around three times, reaching 1.3 billion units, in the five years from 2011. (Fig. 2)
- Rapid increase of space-based PNT such as GPS and Japan’s Quasi-Zenith Satellites System, etc., resulting in expansion of area where global positioning can be measured accurately.
- Based on the above, the United Nations General Assembly has made its first resolution in the field of surveying, committing to improvement of global positioning standards through cooperation with countries all over the world. “Global Geodetic Reference Frame (GGRF)” (Attachments 1 and 2)
- The resolution included support for ability and personnel training required for establishment of standards, accurate position measurement to be carried out responsibly by each nation, etc.
- With this resolution, there is recognition of the need to maintain positioning standards and carry out accurate position measurement, particularly in developing nations, and it is expected that the cutting-edge technology that has been developed by Japan will further advance its overseas expansion.
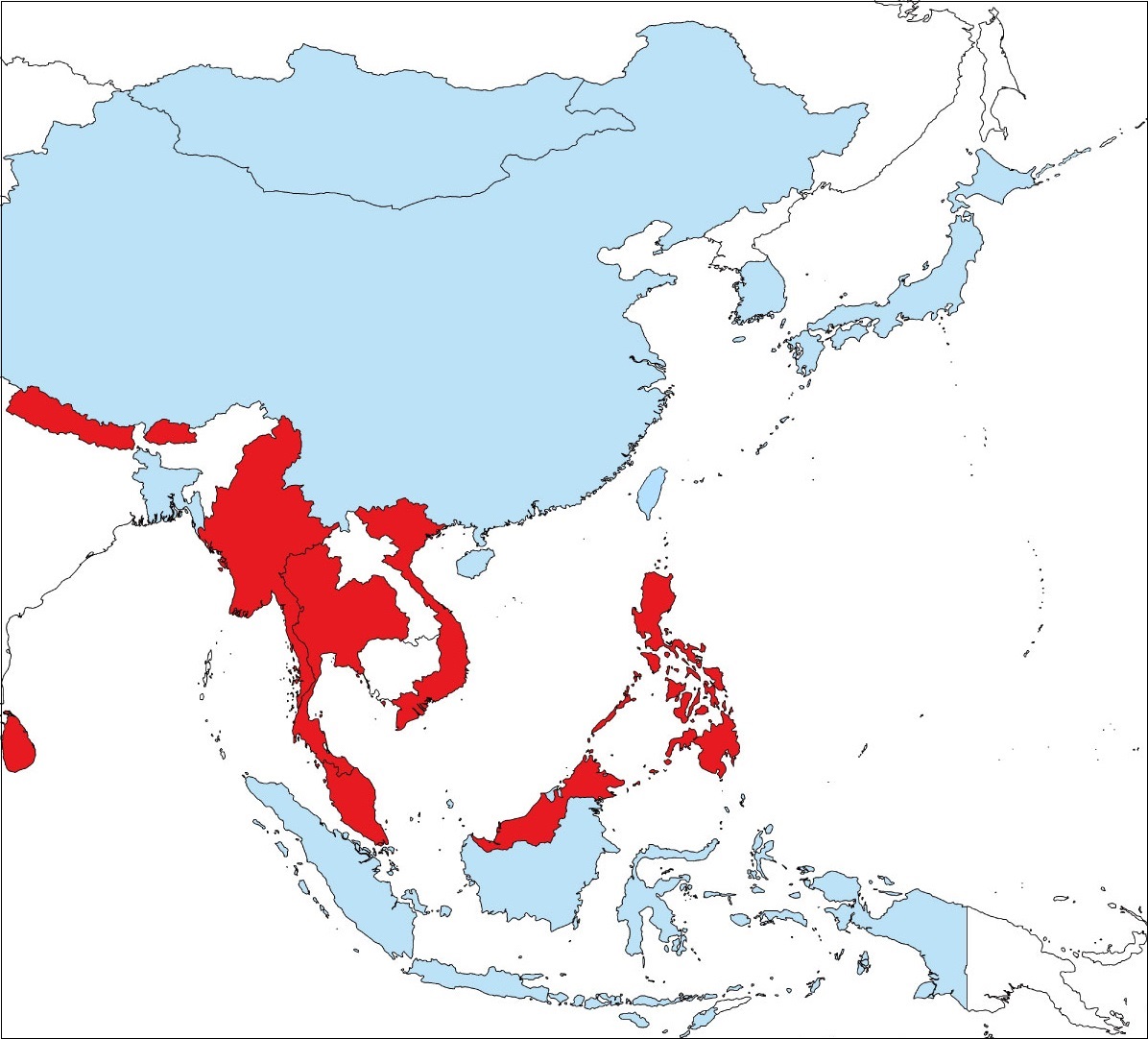
Fig. 1 Adoption of global geodetic reference frame in Asia region
(light blue: adopted, red: not adopted, white: unknown) |
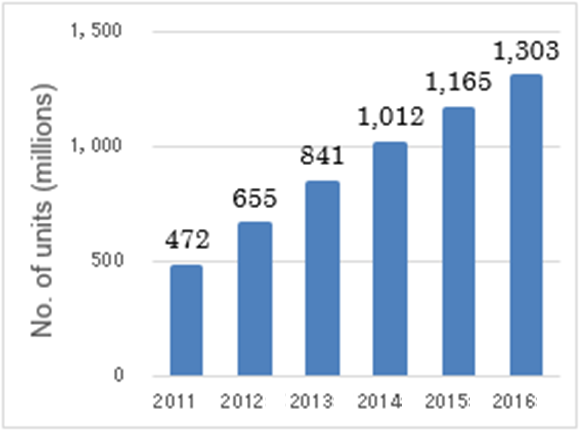
Fig. 2 Estimated number of smartphone sales worldwide
(FY 2012 White Paper Information & Communications ) |
Attachments and Glossary
- Glossary
- Global Geodetic Reference Frame (GGRF)
Positioning standard showing earth shape and changes thereof. Created by integrating various space geodetic observations for earth measurements using space geodetic technology, such as GNSS, etc. Provides positioning information that is essential for accurate positioning in human society and economic activities.
- Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
General term for space-based PNT systems that determine positions by using signals from man-made satellites orbiting the earth.
Leading example is GPS used by the United States of America, but other examples include Japan’s Quasi-Zenith Satellite System, Russia’s GLONASS, the EU’s Galileo and China’s BeiDou, etc., all of which are widely used in surveying and navigation.
|



